|
Cooperative Caching Layer for Scalable Parallel Data Movement in Exascale Supercomputing: Copper
Users of exascale computers like the ALCF’s Aurora—which feature more than 10,000 compute nodes—can experience as much as 20 minutes of idle time for a single line of code during application initialization. Copper, a scalable data loading library developed at the ALCF by an Argonne research team, addresses this problem—reducing load times by as much as 95 percent—by freeing up energy and compute resources. This is achieved without any changes to application codes, by means of a cooperative caching layer.
Challenge
The ALCF’s file system struggled to accommodate requests commensurately with the rate at which users made them, leading to frequent crashes. The researchers responded to this I/O bottleneck by introducing a data loader capable of reducing reducing storage-side congestion: Copper, a read-only cooperative caching layer.
Without the use of algorithms, Copper reduces initialization and loading times by creating a remote procedure call (RPC) overlay network tree with local cache on each node. The root node performs the data loading from the underlying storage system and then distributes to requesting nodes over the ALCF’s Slingshot network.
Performance Results
Copper users merely need to append a prefix to the data path without any application code changes. This simple path change has enabled scaling with near constant data-loading on many thousands of nodes of the Aurora system, as demonstrated in a paper presented at the 2024 Supercomputing Conference. By freeing up highly contended computing resources and network infrastructure with vastly reduced I/O demands, Copper improves performance in numerous ways.
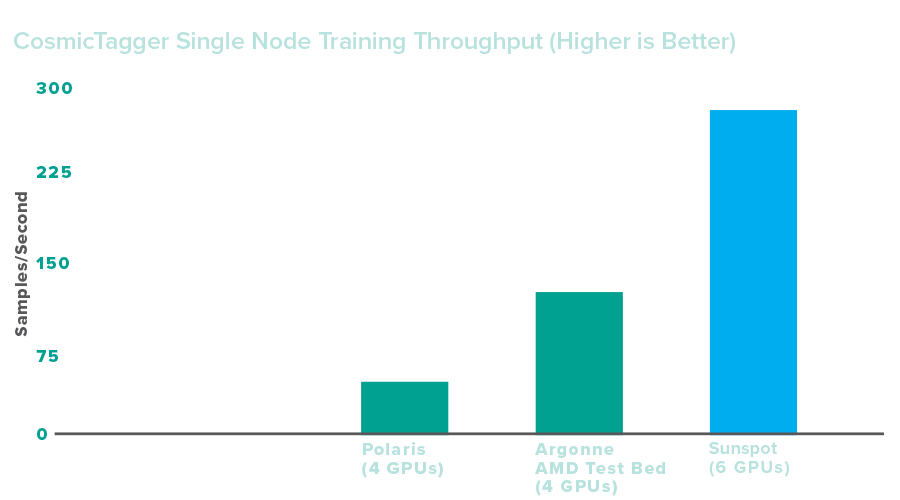
Impact
Copper has not only drastically reduced the total time to load data and software libraries, but has also freed up such previously contended, highly demanded resources such as filesystem responders and storage network bandwidth. The savings in time and energy have enabled the ALCF to permit more science-campaign jobs with more efficient utilization of resources. Copper also provides an effective means to adopt and reuse existing software libraries developed within the DOE laboratory system. The researchers are currently assisting other exascale computing facilities with the deployment of Copper.